Ear correction surgery, also known as Otoplasty, stands out as a remarkable procedure that can bring about significant changes to the appearance of one’s ears. If you’ve ever wondered about the possibilities and considerations associated with this surgery, you’re in the right place. “Dr. Maadico” is your trusted partner for the best ear surgery in Iran.
This article will provide you with a clear, informative overview of ear correction surgery, from what it entails to who it can benefit and why it’s performed.
What Is Otoplasty?
Otoplasty is a popular cosmetic ear surgery designed to modify the shape, position, or size of the ears. This procedure is tailored to address various concerns related to ear aesthetics and can encompass a range of corrections, ranging from subtle adjustments to more comprehensive transformations.
Types of Otoplasty Procedures
Ear correction surgery includes several different procedures. The choice of method depends on the specific issue a patient wants to address. Here are some common types of otoplasty procedures:
| Type of Otoplasty Procedure | Description |
| Ear Pinning (Antihelical Fold Creation) | Reshaping the antihelical fold to bring ears closer to the head, correcting protrusion. |
| Ear Reduction (Earlobe Reduction) | Reducing the size or shape of the earlobes, often for large or elongated earlobes. |
| Ear Augmentation (Earlobe Enlargement) | Augmenting or enlarging the earlobes, sometimes in combination with other procedures. |
| Conchal Setback Otoplasty | Reshaping the conchal bowl to reduce ear projection in individuals with overly prominent ears. |
| Earlobe Rejuvenation | Addressing sagging or aging earlobes by removing excess skin and tissue. |
| Ear Reshaping (Total Otoplasty) | Comprehensive approach addressing both the antihelical fold and the conchal bowl. |
| Ear Reconstruction (Microtia Repair) | Creating a new ear for individuals with microtia, often using rib cartilage or other tissue. |
| Earlobe Repair | Repairing torn, stretched, or gauged earlobes to restore a natural appearance. |
| Combination Procedures | Combining multiple ear surgery techniques to address various issues simultaneously. |
| Revision Otoplasty | Correcting unsatisfactory results from a previous ear surgery, often more challenging due to scar tissue. |
Who Is a Suitable Candidate for Cosmetic Ear Surgery?
A good candidate for ear surgery is someone who meets specific criteria about the appearance of their ears. Here are some key factors that make an individual a suitable candidate for ear correction surgery:
- Otoplasty is commonly performed on children and teenagers, as well as adults. For children, it’s often recommended that they are at least 5 or 6 years old, as their ears have typically reached their full size by that age. It is generally not recommended for infants, as their ears are still developing.
- Otoplasty is suitable for those who have specific concerns about the appearance of their ears, such as prominent or protruding ears, asymmetry, deformities, or dissatisfaction with the shape of their ears.
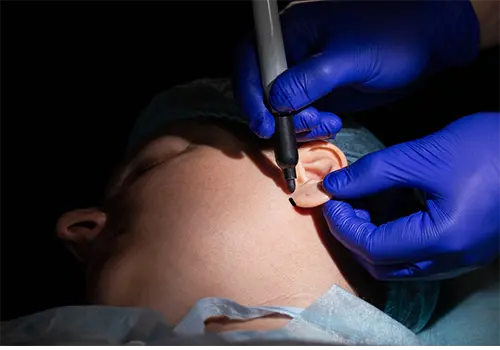
Preparation for the Surgery
Before surgery, it is crucial to make adequate preparations to ensure a smooth and successful surgical experience. Here are some critical aspects of practice:
- Consultation: During this consultation, you will have the opportunity to discuss your goals and concerns regarding your ears. The surgeon will evaluate your ear’s structure, symmetry, and positioning.
- Medical Evaluation: Your surgeon may require a thorough medical evaluation to assess your overall health and fitness for surgery. Be sure to disclose any medical conditions, allergies, medications, or previous surgeries during this assessment.
- Preoperative Instructions: Your surgeon will provide preoperative instructions, which may include dietary restrictions, recommendations regarding medications and supplements to avoid (especially those that can increase the risk of bleeding), and guidelines for smoking cessation if you are a smoker.
During the Surgery
Otoplasty is typically performed as an outpatient procedure and involves the following elements:
Techniques
The surgeon will employ various techniques to reshape the ear cartilage and bring the ears into a more desirable position. Standard methods include:
- Reshaping the cartilage.
- Taking a piece of the patient’s rib cartilage.
- Using ear prostheses or polyethylene plastic implants.
- Pinning back protruding ears.
- Correcting ear asymmetry.
Duration
The surgery typically takes 1 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the correction and the specific technique used.
Anesthesia and Sedation
Otoplasty can be performed under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia. The choice depends on the surgeon’s recommendation and the patient’s comfort.
Steps of Operation
The specific steps may vary slightly based on the individual patient’s needs and the surgeon’s techniques:
Ear Pinning (Otoplasty for Prominent/ Protruding Ears):
- The surgeon makes a small incision on the back of the ear, typically within the natural creases, to minimize visible scarring.
- The surgeon exposes the ear cartilage and carefully reshapes it. This may involve folding the cartilage to reduce ear projection (how far the ear sticks out from the head).
- Permanent sutures are used to hold the reshaped cartilage in its new position, which helps to maintain the ear’s new shape.
- The incisions are closed with fine sutures, and the skin is carefully stitched together to minimize scarring.
- A sterile bandage or dressing is applied to protect the incisions and help maintain the new ear shape.
Ear Reduction (Otoplasty for Large Ears):
- An incision is made on the back of the ear, similar to the incision used in ear pinning.
- Excess cartilage and tissue are carefully removed from the ear to reduce size. The surgeon may also sculpt the remaining cartilage to achieve a balanced appearance.
- Sutures are used to close the incisions and maintain the new ear size and shape.
- A sterile bandage or dressing is applied to protect the incisions and promote proper healing.
Ear Augmentation (Otoplasty for Small or Underdeveloped Ears):
- An incision is carefully made to create the desired shape and size for your ear.
- In some cases, cartilage from your own body, usually from the ribcage, is obtained and inserted into the ear to augment its size and reshape it.
- Fine, dissolvable sutures are used to close the incisions. Over time, these sutures will naturally dissolve, eliminating the need for suture removal.
- A sterile dressing is applied over the incisions to safeguard the surgical area and facilitate proper healing.

Recovery and Aftercare
After the surgery, your postoperative care is crucial for a successful recovery:
Immediate Post-Surgery Recovery (1-2 Days)
- You will have a bandage or dressing over the surgical site. Keep this dressing dry and intact until your surgeon instructs you to remove it.
- You may experience mild discomfort or pain. Your surgeon will prescribe pain medication, and it’s essential to take it as directed for the first few days.
- Rest with your head elevated. This helps reduce swelling and discomfort. Try to sleep on your back for the first few nights.
- Refrain from strenuous activities, bending, or any activities that could strain your surgical site for at least the first week.
Recovery Week 1
- Swelling and bruising are normal. Use cold compresses as directed by your surgeon to reduce these effects.
- Avoid getting your incisions wet, as moisture can interfere with the healing process. If instructed, you can gently clean around the incisions with a mild, non-alcoholic cleanser.
- Continue taking any prescribed medications, such as antibiotics, to prevent infection.
Recovery Weeks 2-6
- If non-absorbable sutures were used, your surgeon typically removes them during follow-up appointments, usually within the first two weeks. Follow your surgeon’s instructions regarding suture care.
- Follow your surgeon’s advice on when you can gradually return to regular activities and exercise. Avoid contact sports or activities where your ears could be injured for a few months.
- Continue to care for your incisions. If your surgeon recommends, use silicone gel or sheets to help minimize scarring.
Long-Term Aftercare (Months to Years)
- Continue to protect your ears from trauma. Consider wearing a headband when playing sports or sleeping, especially in the first few months.
- Shield your ears from direct sun exposure to prevent hyperpigmentation. Use sunscreen or wear a hat when outdoors.
- Maintain regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon as advised to monitor your progress and address any concerns.
- It can take several months for your ears to settle into their new shape fully. Expect subtle changes and improvements over time.
Results and Timeline
The timeline for ear correction surgery results and recovery typically follows these stages:
- Immediate Results: Immediately after the surgery, you will notice a change in the appearance of your ears. However, they will still be swollen, and the final results will take some time to become apparent.
- Swelling and Bruising: Swelling and bruising are common in the first few days and gradually diminish over several weeks. By about 2 to 4 weeks, most of the visible swelling and bruising should have resolved.
- Final Results: The final results of the surgery may become apparent within a few months to a year as the ears settle into their new position and any residual swelling or asymmetry subsides.
- Scarring: Incisions are typically well-concealed behind the ear, and any scarring should fade and become less noticeable over time.

How Long Do the Results Last?
The results of cosmetic ear surgery, such as ear pinning or ear reshaping, are typically long-lasting and often considered permanent, as the procedure is performed once the ears have reached their full size. While natural aging may impact the ears over time, follow-up care and adherence to postoperative instructions can help maintain results for many years.
Are There any Side Effects of Ear Correction Surgery?
Like any surgical procedure, ear correction surgery can have potential side effects and complications, including:
Common side effects
- Swelling and bruising around the ears
- Pain and discomfort
- Itching and numbness
- Redness and tenderness at the incision site
- Temporary changes in sensation
- Scarring (usually minimal)
- Infection (rare, but possible)
- Allergic reactions to anesthesia or surgical materials (rare)
Less common side effects
- Hematoma (collection of blood under the skin)
- Asymmetry or irregular shape of the ears
- Prolonged numbness or altered sensation
- Keloid or hypertrophic scar formation (excessive scarring)
- Persistent pain or discomfort
- Revision surgery may be required
Minimizing Risks of Surgery
- Choose a board-certified and experienced plastic surgeon or otolaryngologist.
- Follow the surgeon’s preoperative and postoperative instructions carefully.
- Avoid smoking and consuming alcohol before and after the surgery.
- Follow a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to optimize overall health and recovery.
- Attend follow-up appointments with your surgeon as scheduled to monitor the healing process and address any concerns promptly.
Last Words
The benefits of ear correction surgery, in terms of appearance and improved self-esteem, can be long-lasting, providing individuals with newfound confidence and satisfaction in their ear aesthetics.
Before considering ear correction surgery, take your time to research and choose a highly qualified and experienced surgeon thoroughly. “Dr. Maadico” can guide you through this journey to newfound confidence and ear aesthetics.
If you’re ready for a change, request a free consultation.
You may also be interested in knowing about:
Chin Reshaping
Facial Bone Contouring
Chin Sculpting Procedures
Jawline Surgery
Facial Scar Revision
Cheek Dimple Creation
Forehead Reduction Procedure
Brow Bone Reduction
Buccal Fat Removal
Facial Feminization
Lip Enhancement
Necklift
FAQ
- Can you get surgery to fix your ears?
Yes, Otoplasty, commonly known as ear correction surgery, can address ear aesthetics and reshape ears.
- Why choose Iran for ear correction surgery?
Iran offers affordable ear correction surgery with skilled surgeons and high-quality healthcare facilities, making it a top choice for medical tourists.
- What is the best age for ear correction surgery?
The best age for ear correction is typically after 5-6 years when the ears have reached their full size, but adults can also undergo the procedure.
- Is ear correction surgery a safe procedure?
When performed by a qualified surgeon, Otoplasty is generally safe with low risks, and it can deliver transformative results.
- How long does it take to recover from ear correction surgery?
Initial recovery may take a few days, but full recovery and visible results typically occur over several weeks to a few months.


